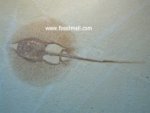
Fossil
Mall maintains an extensive offering of fish fossils for
sale, including many rare and exotic specimens. Visit
these fossil dealer shops currently stocking
Fish
Fossils for Sale:
EDCOPE
Enterprises Fish Fossils I EDCOPE
Enterprises Green River Fish Fossils I Pangaea
Fossils
Some
of the finest fossil fish in the world come from the Cretaceous
Lagerstatt in Lebanon. See a broad selection
of these Lebanese
Fossil Fish and those from the Bear Gulch Limestone at
EDCOPE Enterprises.
Taxonomy
for Fish Fossils
Subclass Pteraspidomorphi (early jawless fish)
Class Thelodonti
Class Anaspida
(unranked) Cephalaspidomorphi (early jawless fish)
(unranked) Hyperoartia
Petromyzontidae (lampreys)
Class Galeaspida
Class Pituriaspida
Class Osteostraci (bony armored jawless fis)
Infraphylum Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates)
Class Placodermi (extinct)
Class Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish)
Class Acanthodii (spiny sharks. extinct)
Superclass Osteichthyes (bony fish)
Class Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish)
Class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish)
Subclass Coelacanthimorpha (coelacanths)
Subclass Dipnoi (lungfish)
Subclass Tetrapodamorpha
|
 Fish
comprise a paraphyletic group (containing taxa that
are descended from a common ancestor, but not including all
taxa descended from the common ancestor), including hagfishes,
lampreys, sharks and rays, ray-finned fishes, coelacanths,
and lungfishes. More formally, fishes are any non-tetrapod
chordates. One widely accepted taxonomy is shown to the right,
and some brief descriptions are given below for major groups
from which fossils are known.
Fish
comprise a paraphyletic group (containing taxa that
are descended from a common ancestor, but not including all
taxa descended from the common ancestor), including hagfishes,
lampreys, sharks and rays, ray-finned fishes, coelacanths,
and lungfishes. More formally, fishes are any non-tetrapod
chordates. One widely accepted taxonomy is shown to the right,
and some brief descriptions are given below for major groups
from which fossils are known.
 The Agnatha are
the jawless fish, and the extant varieties are the last survivors
of the world's first vertebrate animals. The jawless fish
diverged from other fish during the Cambrian some 500 million
years ago, and lack scales, paired fins, and jaws. They instead
have a circular toothed outgrowth used to latch on to the
side of another fish in order to feed on its blood.
Agnatha were prominent among primitive fishes of the early
Paleozoic. Haikouichthys and Myllokunmingia are notable agnathans
from the Chengjiang biota of China. Another putative agnathid
from Chengjiang is Haikouella. The Agnatha larvae are filter
feeders, a characteristic that betrays their evolutionary
kinship with invertebrate chordates. Many Ordovician, Silurian,
and Devonian agnathans were heavily armored with bony, spiked
plates. The Ostracoderms were the first armored agnathans,
ancesctors of the bony fish and thus to tetrapods, including
humans, beings) that are are known from the middle Ordovician.
Agnathans never recovered from a decline during the Devonian.
The Agnatha are
the jawless fish, and the extant varieties are the last survivors
of the world's first vertebrate animals. The jawless fish
diverged from other fish during the Cambrian some 500 million
years ago, and lack scales, paired fins, and jaws. They instead
have a circular toothed outgrowth used to latch on to the
side of another fish in order to feed on its blood.
Agnatha were prominent among primitive fishes of the early
Paleozoic. Haikouichthys and Myllokunmingia are notable agnathans
from the Chengjiang biota of China. Another putative agnathid
from Chengjiang is Haikouella. The Agnatha larvae are filter
feeders, a characteristic that betrays their evolutionary
kinship with invertebrate chordates. Many Ordovician, Silurian,
and Devonian agnathans were heavily armored with bony, spiked
plates. The Ostracoderms were the first armored agnathans,
ancesctors of the bony fish and thus to tetrapods, including
humans, beings) that are are known from the middle Ordovician.
Agnathans never recovered from a decline during the Devonian.
 The Chondrichthyes are
the cartilaginous fish having flexible skeleton of cartilage
rather than bone. They evolved some 100 million years after
the jawless fish and the sharks, skates, and rays. They have
jaws, teeth and scales, and are, in general, effective predators.
The teeth of carnivorous sharks are not attached to the jaw,
but instead are embedded in the flesh. Shark teeth of many
species are constantly replaced and some sharks can lose
30,000 teeth over their lifetime, which is why shark teeth
fossils are so abundant. In contrast, cartilagage poorly
fossilizes, making the cartilaginous fish fossils relatively
uncommon.
The Chondrichthyes are
the cartilaginous fish having flexible skeleton of cartilage
rather than bone. They evolved some 100 million years after
the jawless fish and the sharks, skates, and rays. They have
jaws, teeth and scales, and are, in general, effective predators.
The teeth of carnivorous sharks are not attached to the jaw,
but instead are embedded in the flesh. Shark teeth of many
species are constantly replaced and some sharks can lose
30,000 teeth over their lifetime, which is why shark teeth
fossils are so abundant. In contrast, cartilagage poorly
fossilizes, making the cartilaginous fish fossils relatively
uncommon.
 The Osteichthyes are
the bony fish that evolved in conjunction with the cartilaginous
fish that are by far the largest group of fishes, have paired
fins, dermal scales, numerous vertebrae, and often many teeth.
The bony fish (Osteichthyes) can, in turn, be divided into
two categories, the lobe-finned fish and the ray-finned fish.
Lobe-finned fish have muscular fins supported by bones. The
lone surviving lobe-finned fish is the coelacanth. Science
believes that terrestrial animals evolved from lobe-finned,
rather than ray-finned fish. Ray-finned fish comprise all
other fish with a flexible skeleton made of bone. Osteichthyes
are the largest group of vertebrates comprising some 29,000
extant species.
The Osteichthyes are
the bony fish that evolved in conjunction with the cartilaginous
fish that are by far the largest group of fishes, have paired
fins, dermal scales, numerous vertebrae, and often many teeth.
The bony fish (Osteichthyes) can, in turn, be divided into
two categories, the lobe-finned fish and the ray-finned fish.
Lobe-finned fish have muscular fins supported by bones. The
lone surviving lobe-finned fish is the coelacanth. Science
believes that terrestrial animals evolved from lobe-finned,
rather than ray-finned fish. Ray-finned fish comprise all
other fish with a flexible skeleton made of bone. Osteichthyes
are the largest group of vertebrates comprising some 29,000
extant species.



 The Chondrichthyes are
the cartilaginous fish having flexible skeleton of cartilage
rather than bone. They evolved some 100 million years after
the jawless fish and the sharks, skates, and rays. They have
jaws, teeth and scales, and are, in general, effective predators.
The teeth of carnivorous sharks are not attached to the jaw,
but instead are embedded in the flesh. Shark teeth of many
species are constantly replaced and some sharks can lose
30,000 teeth over their lifetime, which is why shark teeth
fossils are so abundant. In contrast, cartilagage poorly
fossilizes, making the cartilaginous fish fossils relatively
uncommon.
The Chondrichthyes are
the cartilaginous fish having flexible skeleton of cartilage
rather than bone. They evolved some 100 million years after
the jawless fish and the sharks, skates, and rays. They have
jaws, teeth and scales, and are, in general, effective predators.
The teeth of carnivorous sharks are not attached to the jaw,
but instead are embedded in the flesh. Shark teeth of many
species are constantly replaced and some sharks can lose
30,000 teeth over their lifetime, which is why shark teeth
fossils are so abundant. In contrast, cartilagage poorly
fossilizes, making the cartilaginous fish fossils relatively
uncommon.  The Osteichthyes are
the bony fish that evolved in conjunction with the cartilaginous
fish that are by far the largest group of fishes, have paired
fins, dermal scales, numerous vertebrae, and often many teeth.
The bony fish (Osteichthyes) can, in turn, be divided into
two categories, the lobe-finned fish and the ray-finned fish.
Lobe-finned fish have muscular fins supported by bones. The
lone surviving lobe-finned fish is the coelacanth. Science
believes that terrestrial animals evolved from lobe-finned,
rather than ray-finned fish. Ray-finned fish comprise all
other fish with a flexible skeleton made of bone. Osteichthyes
are the largest group of vertebrates comprising some 29,000
extant species.
The Osteichthyes are
the bony fish that evolved in conjunction with the cartilaginous
fish that are by far the largest group of fishes, have paired
fins, dermal scales, numerous vertebrae, and often many teeth.
The bony fish (Osteichthyes) can, in turn, be divided into
two categories, the lobe-finned fish and the ray-finned fish.
Lobe-finned fish have muscular fins supported by bones. The
lone surviving lobe-finned fish is the coelacanth. Science
believes that terrestrial animals evolved from lobe-finned,
rather than ray-finned fish. Ray-finned fish comprise all
other fish with a flexible skeleton made of bone. Osteichthyes
are the largest group of vertebrates comprising some 29,000
extant species.